Knock Out/KO IFS FOOD Version 8 and the scoring System
Knock Out Criteria IFS FOOD Version 8. Let’s explore IFS Food version 8’s Knock Out criteria and clarify them.
IFS Scoring System IFS Food version 8
Ensuring food safety and quality is vital in the industry. International standards like IFS play a crucial role. In this article, we’ll explore the IFS scoring system and KO criteria used to assess compliance with IFS Food Requirements.
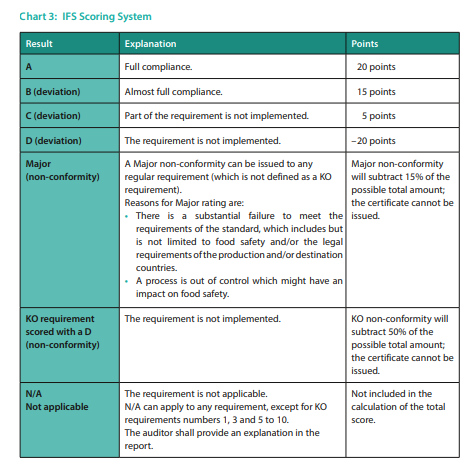
The IFS Scoring System plays a crucial role in determining compliance with the IFS Food Standard. Auditors utilize this comprehensive scoring system to assess companies based on their level of compliance with each requirement. The evaluation ranges from full compliance to deviation or non-conformity.
Throughout the evaluation process, auditors meticulously scrutinize each requirement, taking into account its effectiveness in ensuring food safety. Moreover, they evaluate the measures implemented by the company to meet these requirements. The effectiveness of these measures is vital as they directly influence food safety, compliance with legal requirements, and customer agreements in production and destination countries.
Scoring Possibilities in IFS Food Standard
The IFS Food Standard incorporates six (6) scoring possibilities. Additionally, there is the option of non-applicability for certain requirements. Points are assigned for each requirement based on a scoring chart, which helps auditors gauge compliance levels accurately (see chart 3).
IFS Food version 8 KO requirements
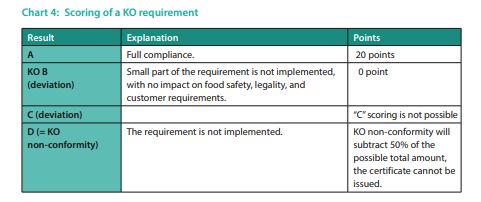
There are specific requirements in the IFS Food Standard known as KO requirements. These essential requirements address key topics needed for compliance. In the IFS Food Standard, there are ten (10) defined KO requirements:
KO1) 1.2.1 Governance and commitment
KO2) 2.3.9.1 Monitoring system of each CCP
KO3) 3.2.2 Personal hygiene
KO4) 4.1.3 Customer agreement
KO5) 4.2.1.3 Raw material specifications
KO6) 4.12.1 Foreign material risk mitigation
KO7) 4.18.1 Traceability
KO8) 5.1.1 Internal audits
KO9) 5.9.1 Procedures of recalls, withdrawals and incidents
KO10) 5.11.3 Corrective actions
The scoring of KO requirements is explained in the following chart (chart 4).
The auditor plays a critical role in granting certification. If they raise Major or KO non-conformities, certification is not granted. For recertification, the current IFS Certificate is withdrawn, following specific rules.
Furthermore, the certification body promptly withdraws the certificate from the IFS Database, usually within two working days after the last audit day. They provide explanations in English, specifying the reasons for withdrawal and the non-conformity numbers in the IFS Database, similar to the action plan details.
Moreover, when there are numerous requirements deemed inapplicable, using a total number of points for the audit can be misleading. Therefore, the IFS Scoring System relies on a percentage of the total available score to determine the production site’s certification status, i.e., foundation or higher level.
To calculate the total score, they multiply the difference between the total number of IFS Food Requirements (points) and those evaluated as not applicable (points) by twenty (20).
Ultimately, they determine the final score, expressed as a percentage, based on the number of points awarded out of the total number of points.
In the audit report, the auditor must provide explanations for requirements classified as compulsory fields (even if scored with A), those scored with B, C, D, Major/KO non-conformities, and requirements audited as not applicable.
Knock Out Criteria IFS FOOD Version 8
Let’s explore IFS Food version 8’s Knock Out criteria and clarify them.
Knock out/KO #1
1.2.1* The senior management shall ensure that employees are aware of their responsibilities related to food safety and product quality and that mechanisms are implemented to monitor the effectiveness of their operation. Such mechanisms shall be identified and documented.
The top management must ensure that employees understand their roles in food safety and quality. Additionally, they should implement and document mechanisms to monitor operations effectively.
Knock out/KO #2
2.3.9.1* Specific monitoring procedures in terms of method, frequency of measurement or observation and recording of results, shall be documented, implemented and maintained for each CCP, to detect any loss of control at that CCP. Each defined CCP shall be under control. Monitoring and control of each CCP shall be demonstrated by records.
To keep critical control points (CCPs) under control, you must have clear monitoring procedures. These procedures include the method, frequency of measurement or observation, and recording results. Records should demonstrate the monitoring and control of each CCP.
Knock out/KO #3
3.2.2* The requirements for personal hygiene shall be understood and applied by all relevant personnel, contractors and visitors.
All involved parties, including employees, contractors, and visitors, must understand and comply with personal hygiene requirements.
Knock out/KO #4
4.1.3* Where there are customer agreements related to:
- product recipe (including raw materials characteristics)
- process
- technological requirements
- testing and monitoring plans
- packaging
- labelling
these shall be complied with.
You must follow customer agreements for product recipe, process, testing, etc., if they exist.
Knock out/KO #5
4.2.1.3* Specifications shall be documented and implemented for all raw materials (ingredients, additives, packaging materials, rework). Specifications shall be up to date, unambiguous and in compliance with legal requirements and, if defined, with customer requirements.
You must create written specifications for all raw materials (ingredients, additives, etc.). These specs should be current, clear, and compliant with legal and customer requirements.
Knock out/KO #6
4.12.1* Based on risks, procedures shall be documented, implemented and maintained to prevent contamination with foreign materials. Contaminated products shall be treated as non-conforming products.
Based on risks, you need procedures to prevent foreign material contamination. If products are contaminated, they are considered non-conforming.
Knock out/KO #7
4.18.1* A traceability system shall be documented, implemented and maintained that enables the identification of product lots and their relation to batches of raw materials, and food contact packaging materials, and/or materials carrying legal and/or relevant food safety information. The traceability system shall incorporate all relevant records of:
- receipt
- processing at all steps
- use of rework
- distribution.
Traceability shall be ensured and documented until delivery to the customer.
You must establish a traceability system that identifies product lots, raw materials, and packaging. This system includes records of receipt, processing, rework, and distribution. Ensure and document traceability until delivery to the customer.
Knock out/KO #8
5.1.1* An effective internal audit program shall be documented, implemented and maintained and shall ensure, at a minimum, that all the requirements of the IFS Standard are audited. This activity shall be planned within a 12-month period and its execution shall not exceed 15 months. The company shall have a risk assessment in place where activities, which are critical to food safety and product quality shall be audited more frequently. It shall also apply to off-site storage locations owned or rented by the company.
You need an internal audit program to check all IFS Standard requirements. It should be documented and implemented within 12 months, not exceeding 15 months. For critical food safety activities, more frequent audits are required. This includes off-site storage locations owned or rented by the company.
Knock out/KO #9
5.9.1* An effective procedure shall be documented, implemented and maintained for the management of recalls, withdrawals, incidents and potential emergency situations with an impact on food safety, product quality, legality and authenticity. It shall include, at a minimum:
- the assignment of responsibilities
- the training of the responsible persons
- the decision-making process
- the nomination of a person, authorised by the company and permanently available, to initiate the necessary process in a timely manner
- an up-to-date alert contact list including customer information, sources of legal advice, available contacts
- a communication plan including customers, authorities and where applicable, consumers
You need to document a procedure for managing recalls, incidents, and emergencies affecting food safety and quality. This procedure must include responsibilities, training, decision-making, designating a person to initiate the process promptly, an updated contact list, and a communication plan involving customers, authorities, and consumers when necessary.
Knock out/KO #10
5.11.3* Corrective actions shall be formulated, documented and implemented as soon as possible to avoid the further occurrence of deviations and non-conformities. The responsibilities and the timescales for corrective actions shall be defined.
You need to quickly formulate, document, and implement corrective actions to prevent future deviations and non-conformities. Assign responsibilities and set timeframes for these actions.
IFS requirement 4.6.1 Adaptive Environmental Monitoring Scheme
The IFS Food v8 introduces a change with requirement 4.6.1. We’ve designed a one-pager to guide you in creating your own Adaptive Environmental Monitoring Scheme.
Click here to download the one-pager.
